Hint for Section 1.3 Question 1c: Invalid argument approach
1c) Let c represent "the cat fiddled", let j
represent "the cow jumped over the moon", let d represent "the
little dog laughed", and let r represent "the dish ran away with the
spoon." Now write each of the premises and the conclusion in symbolic form.
The first premise (p1) is "If the cat fiddled or the cow
jumped over the moon, then the little dog laughed." This can be written symbolically
as (c V j) 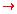 d.
d.
The second premise (p2) is "If the little dog laughed, then the dish ran
away with the spoon." This can be written symbolically as d
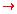 r.
r.
The third premise (p3) is "But the dish did not run away with the
spoon." This can be written symbolically as ~r.
The conclusion (q) is "Therefore the cat did not fiddle." This can be written
symbolically as ~c.
Remember that an argument is written as a conjunction of the premises
implies the conclusion. So this argument can be represented as
[(c V j) 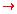 d) L (d
d) L (d 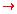 r)
L (~r)]
r)
L (~r)] 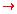 (~c).
(~c).
To determine if it is possible for an argument to be invalid, we are looking for truth
values for the variables which make the conclusion false but all of the premises true.
Fill in the following sentence:
For the conclusion ~c to be FALSE, we need c to be _________.
For the premises to be TRUE we need:
- (c V j)
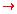 d to be true (1);
d to be true (1);
- d
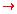 r to be true (2);
r to be true (2);
- ~r to be true (3).
Can you find a set of truth values for c, j, d
and r, which make the conclusion false but the premises true?
Next hint please
Back to Section 1.3
Full solution